

Pharmaceutical development, development and validation of analytical procedures for quality control, preparation of regulatory documentation for the pharmaceutical industry
Study of disperse systems with liquid dispersion medium
The type and parameters of the EPR spectra in true solutions and micellar solutions of surfactants were found to differ and depend on the structure of solutions and micelles as well as on the spin probes’ characteristics. It was demonstrated that surfactant micelles were anisotropic in viscosity, and different segments of the alkyl chains of surfactant-modelling probes possessed divergent dynamic properties. The packing of molecules in micelles was found to be more ordered and compacted at the level of the 5th carbon atom. The alterations in EPR spectra and/or their parameters could be attributable to the interactions of surfactant and probe, surfactant and other dissolved substances, and the thermo-reversible transitions sol↔gel in solutions of poloxamers.
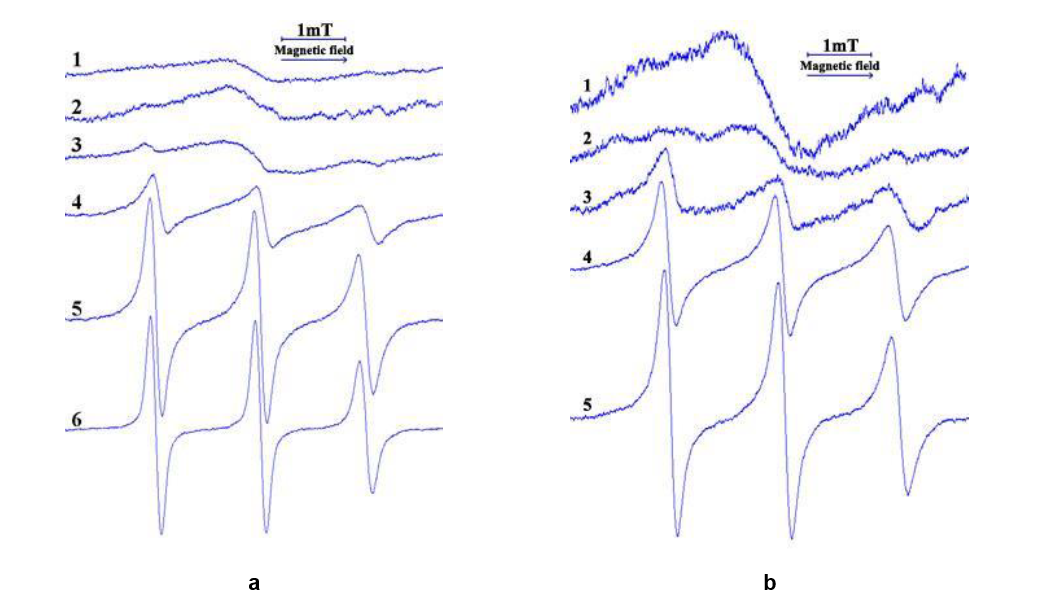
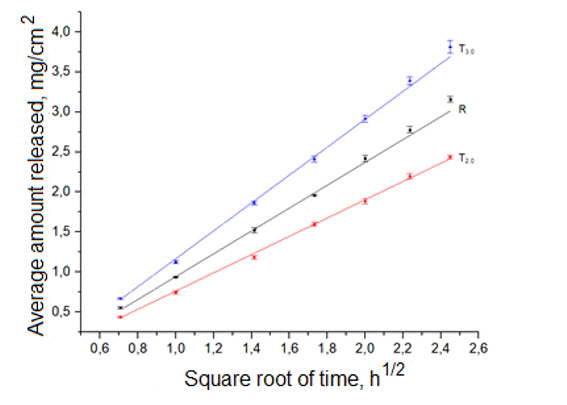
It has been demonstrated that the formation of a carbomer-based gel did not impact the rotational correlation time of the probe, which exhibited no interaction with the carbomer. The release parameters of the dissolved active substance from gels in in vitro experiments were little affected by the difference in apparent viscosity of the gels. The in vitro release of active substance was found to be contingent upon its concentration and the content of hydrophilic non-aqueous solvent.
Study of binary and ternary mixed solvents
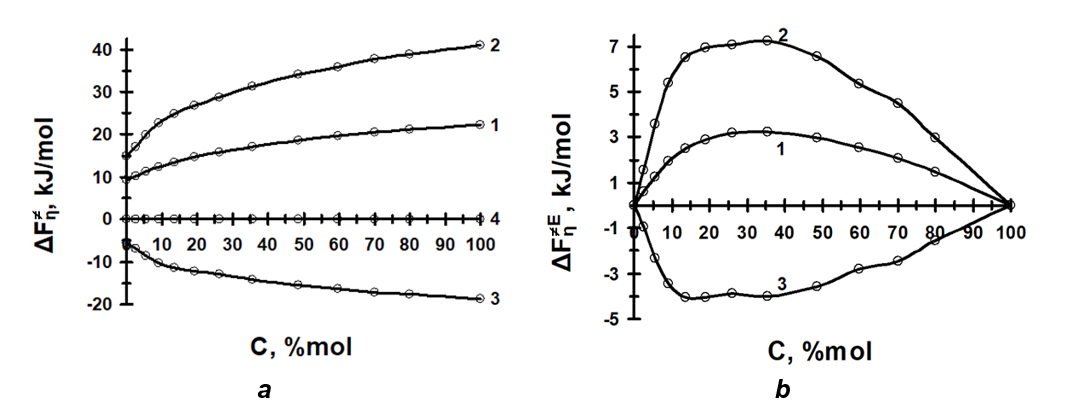
The density, viscosity and thermodynamics of viscous flow of binary and ternary mixed solvents (for example, water – hexylene glycol, water – ethanol – methylpyrrolidone, water – propylene glycol – macrogol 400, propylene glycol – macrogol 400, propylene glycol – water, etc.) have been studied. The relationship between the structure of the mixed solvent systems and the solubility of some active substances (mometasone furoate, betamethasone dipropionate, meloxicam etc.), the physical stability of the emulsions o/w as well as in vitro release of penetration enhancers and active substances have been demonstrated.
The laboratory has over 30 years of experience in applied research on pharmaceutical development and the analysis of medicines. During this period, more than a hundred medicinal products were developed, the majority of which are now produced on a large scale by the Ukrainian pharmaceutical industry.

The standardisation activities encompass the establishment of the standardisation system for the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, the development of numerous guidelines for the Ministry of Health of Ukraine to regulate the pharmaceutical sector (e.g. guidelines on pharmaceutical development, GMP, GDP, etc.), and the involvement of the scientists of the laboratory in the development of some general monographs of the State Pharmacopoeia of Ukraine.

Services for pharmaceutical industry: